CNC Laser cutting Vs Waterjet and Plasma cutting
Laser cutting vs waterjet vs plasma cutting
- Cutting is one of the most important steps in modern manufacturing. Whether it’s shaping sheet metal for an automotive component or carving out detailed patterns for signage, the cutting method you go with has a direct impact on cost, quality, and overall efficiency
- In today’s industry, three methods stand out the most: CNC laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and plasma cutting. Each one comes with its own advantages and trade-offs, and knowing which technique fits your project best can make the difference
- If you’re searching for “laser cutting near me” or exploring CNC laser cutting services in Pune, this guide will let you understand how laser cutting compares with other cutting technologies, and why it may be the right fit for your needs.
Best Laser cutting services by Cyclotron Industries. We offer high precision, fast and accurate laser cutting solutions for any kind of metal applications

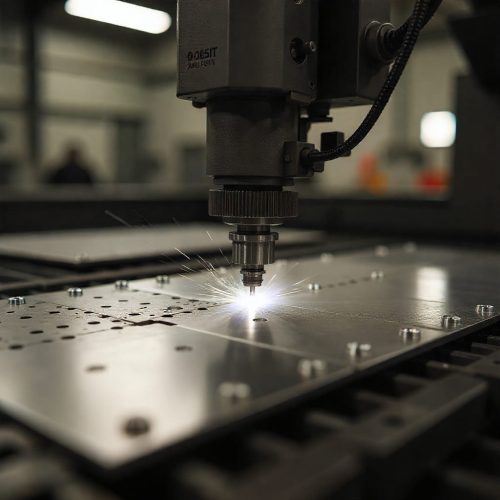
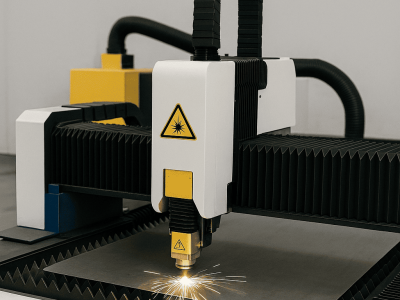
What is CNC Laser Cutting?
- CNC laser cutting is a machining process where a very strong, narrow laser beam is aimed at a small spot on the workpiece. The heat is so intense that it melts or vaporizes the material in that area, removing it and leaving behind a smooth and precise finish. Because the process is CNC-controlled, it can execute intricate shapes and fine details repeatedly with minimal error. This makes metal laser cutting services a go-to choice for industries that demand accuracy and efficiency.
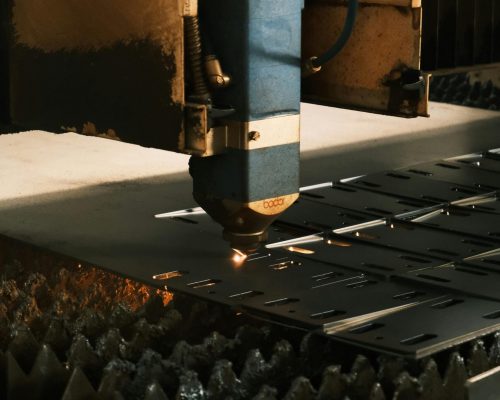

- The laser source generates a concentrated beam of light.
- With the help of mirrors and lenses, this beam is directed and focused onto a tiny point on the material surface.
- The material quickly absorbs the energy, causing it to heat up, melt, or even vaporize at that point.
- At the same time, gases like oxygen, nitrogen, or even compressed air are blown through the cut to clear away melted material. This leaves a clean edge behind.
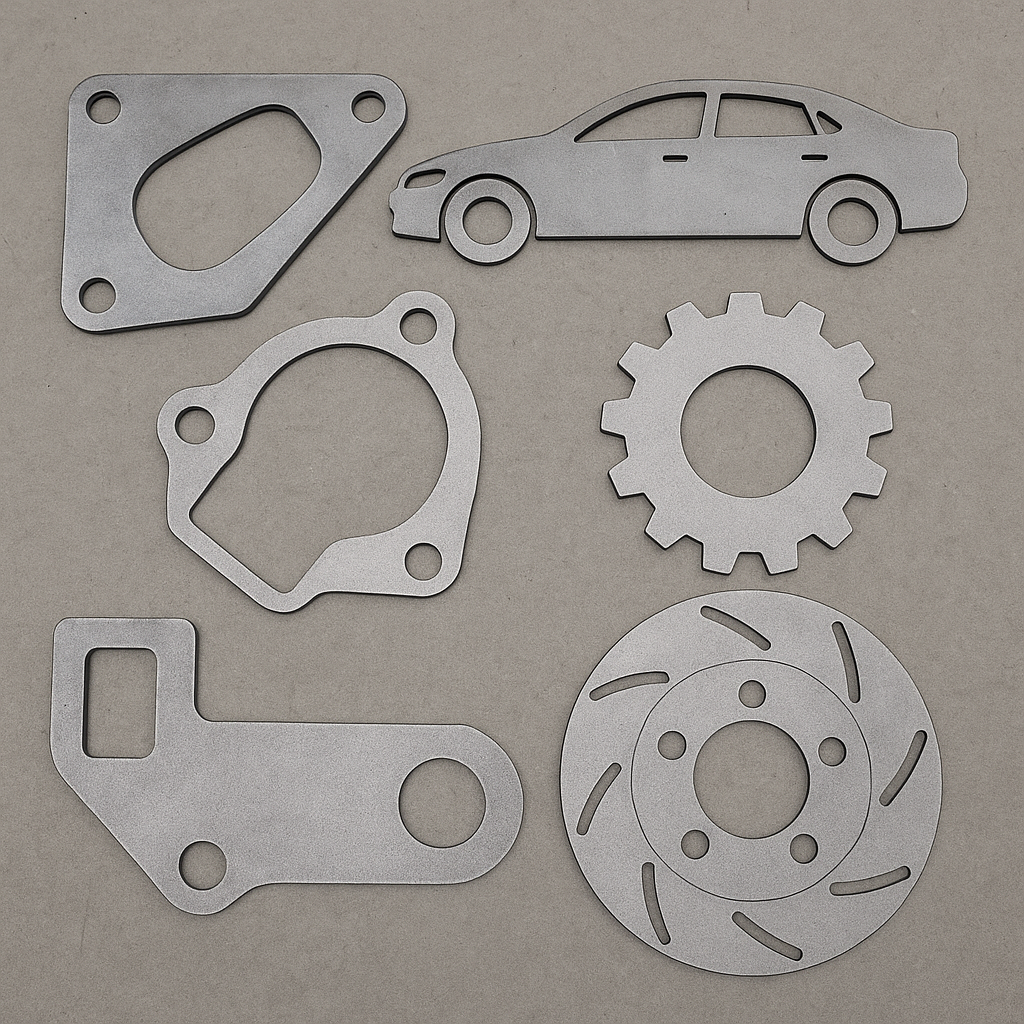
Applications of Laser cutting: Laser cutting is used a lot in sheet metal fabrication, automotive parts, aerospace components, and even in medical device manufacturing. You’ll also find it being applied in signage, jewelry, interior decor, and electronics. Put simply, whenever accuracy and clean detail matter most, laser cutting is usually the method people turn to.
Materials used in laser cutting: It handles metals like steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium easily. Apart from metals, laser cutting also works on non-metal materials such as wood, plastics, leather, textiles, rubber, paper, and some composites.
If you’re in Pune and searching for laser cutting in Pune for precise industrial parts or creative designs, CNC laser technology is likely your best option.
For detailed information of working on laser cutting refer this blog (More info)
What is Waterjet Cutting?
As the name says, waterjet cutting is a precise cutting method where water under extremely high pressure (sometimes up to 90,000 PSI) is sprayed at the workpiece. To improve the cutting power, abrasive particles are often mixed into the stream, allowing it to slice through even hard materials.
- The process starts with a pressure pump that builds water pressure far higher than what comes out of a normal hose.
- This water is then pushed through a tiny nozzle, usually made from materials like sapphire or ruby, to form a high-speed jet.
- The velocity of the stream is so high that it can cut through many materials directly.
- When tougher materials like metals, ceramics, or composites are involved, abrasive particles (commonly garnet) are added into the water stream. This creates a sandblasting effect that helps cut through them.
- The cutting head can be moved in different directions, making it possible to achieve fine details and complex shapes.
Applications of Waterjet cutting: Waterjet cutting finds its place in aerospace, automotive, architecture, and also in the stone and marble industries. It’s especially popular for glass cutting, custom fabrication, artistic designs, and prototypes where heat damage just can’t be allowed.
Materials: It can cut almost any material, including metals, stone, ceramics, composites, glass, plastics, rubber, and even food products. This makes it one of the most versatile cutting technologies available.
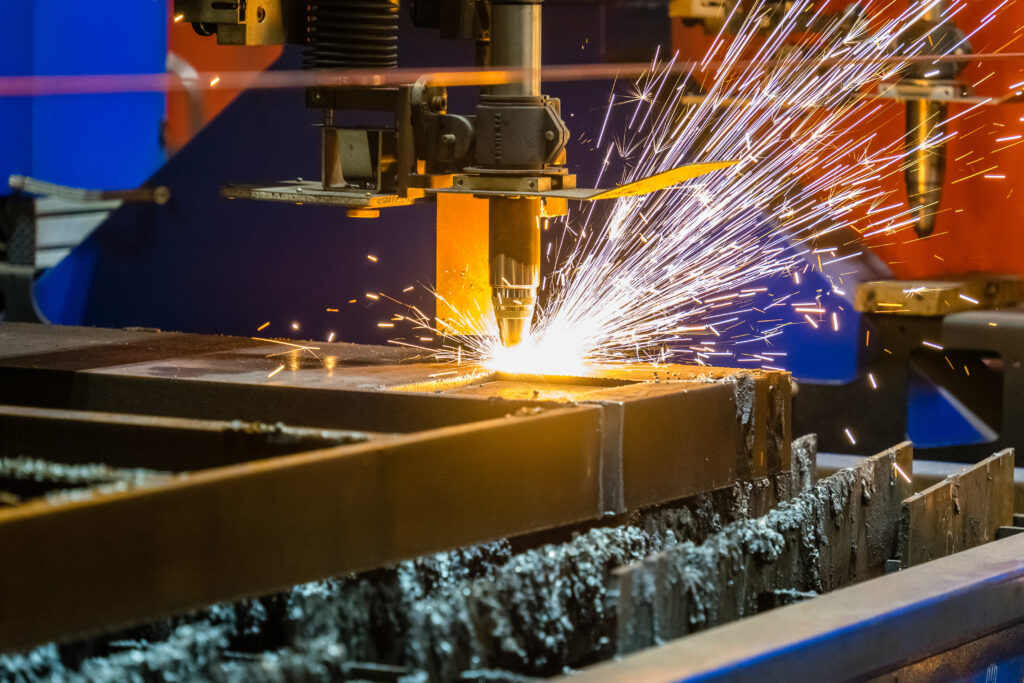
What is Plasma Cutting?
Plasma cutting works by directing a jet of ionized gas, heated to over 20,000°C, onto the material you want to cut. The intense heat melts the material, and the force of the gas blows the molten material away, leaving a clean cut. Gases like argon, argon mixed with hydrogen, or nitrogen are typically used in the process.
- Inside the plasma torch, an electric arc is created.
- This arc passes through a stream of gas moving through a copper nozzle.
- The gas becomes ionized, turning into plasma—a hot, electrically conductive state of matter.
- The plasma jet cuts into the material, while compressed gas removes the molten metal from the cut path.
Applications of Plasma cutting: Plasma cutting is used in industries like metal fabrication, automotive repair, shipbuilding, and construction. It’s especially useful for fast cutting of sheet metal, pipes, and structural components. - Materials: The method is effective only on electrically conductive materials, making it best for metals such as mild steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. It can handle both thin sheets and thicker metal sections with good efficiency.
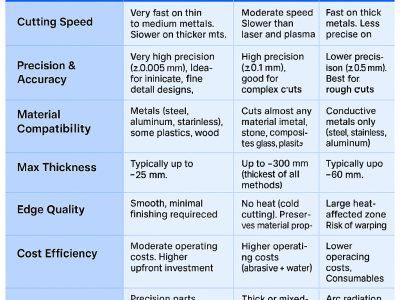
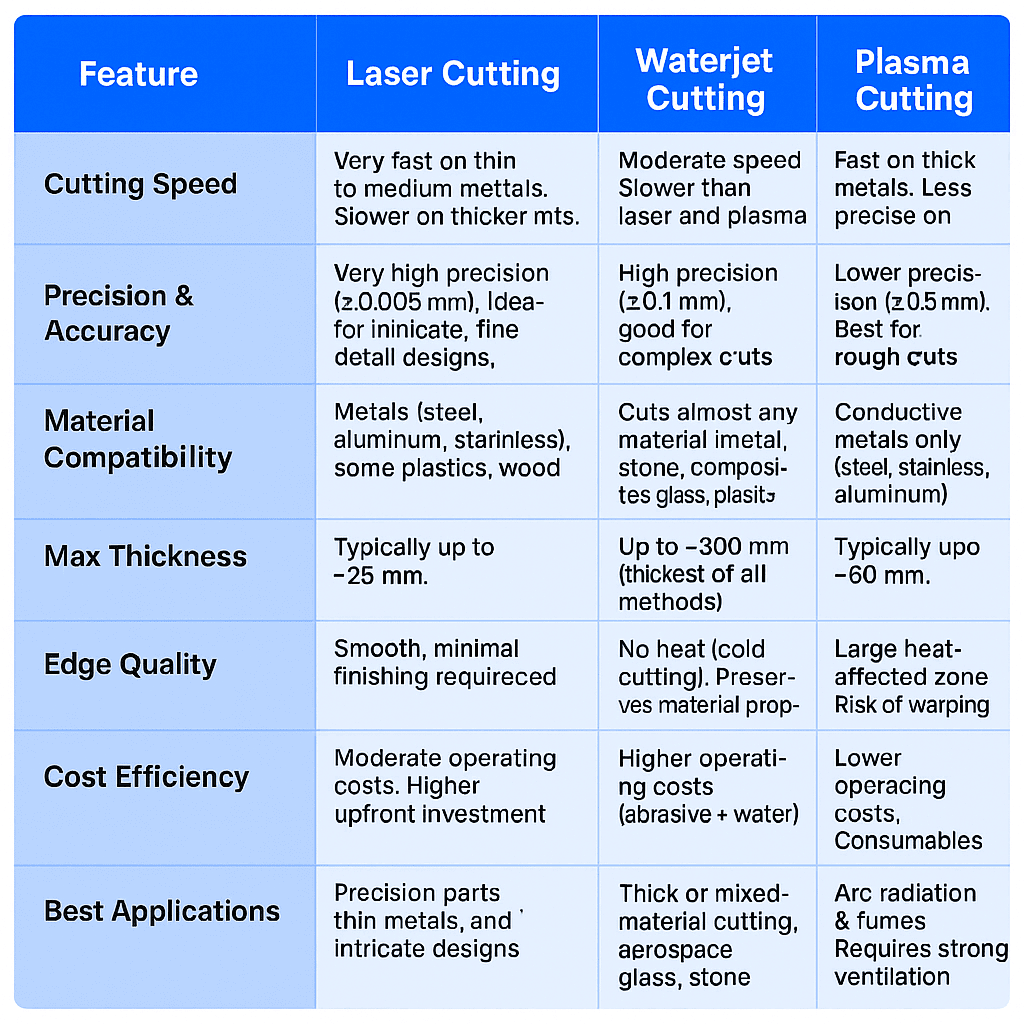
| Feature | Laser Cutting | Waterjet Cutting | Plasma Cutting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | Very fast on thin to medium metals. Slower on thicker materials. | Moderate speed. Slower than laser and plasma. | Fast on thick metals. Less precise on thin sheets. |
| Precision & Accuracy | Very high precision (±0.005 mm). Ideal for intricate, fine detail designs. | High precision (±0.1 mm); good for complex cuts. | Lower precision (±0.5 mm). Best for rough cuts. |
| Material Compatibility | Metals (steel, aluminum, stainless), some plastics, wood. | Cuts almost any material (metal, stone, composites, glass, plastics). | Conductive metals only (steel, stainless, aluminum). |
| Max Thickness | Typically up to ~25 mm. | Up to ~300 mm (thickest of all methods). | Typically up to ~50 mm. |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, minimal finishing required. | Smooth, no heat-affected zone. | Rougher edges may require post-processing. |
| Heat Impact | Heat-affected zone present. Not ideal for heat-sensitive materials. | No heat (cold cutting). Preserves material properties. | Large heat-affected zone. Risk of warping. |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate operating costs. Higher upfront investment. | Higher operating costs (abrasive + water). | Lower operating costs. Consumables inexpensive. |
| Best Applications | Precision parts, thin metals, and intricate designs. | Thick or mixed-material cutting, aerospace, glass, stone. | Structural steel, construction, heavy fabrication. |
| Safety & Environment | Laser hazards (eye/skin protection), fumes require extraction. | High water/abrasive waste. Higher environmental impact if not managed. | Arc radiation & fumes. Requires strong ventilation. |
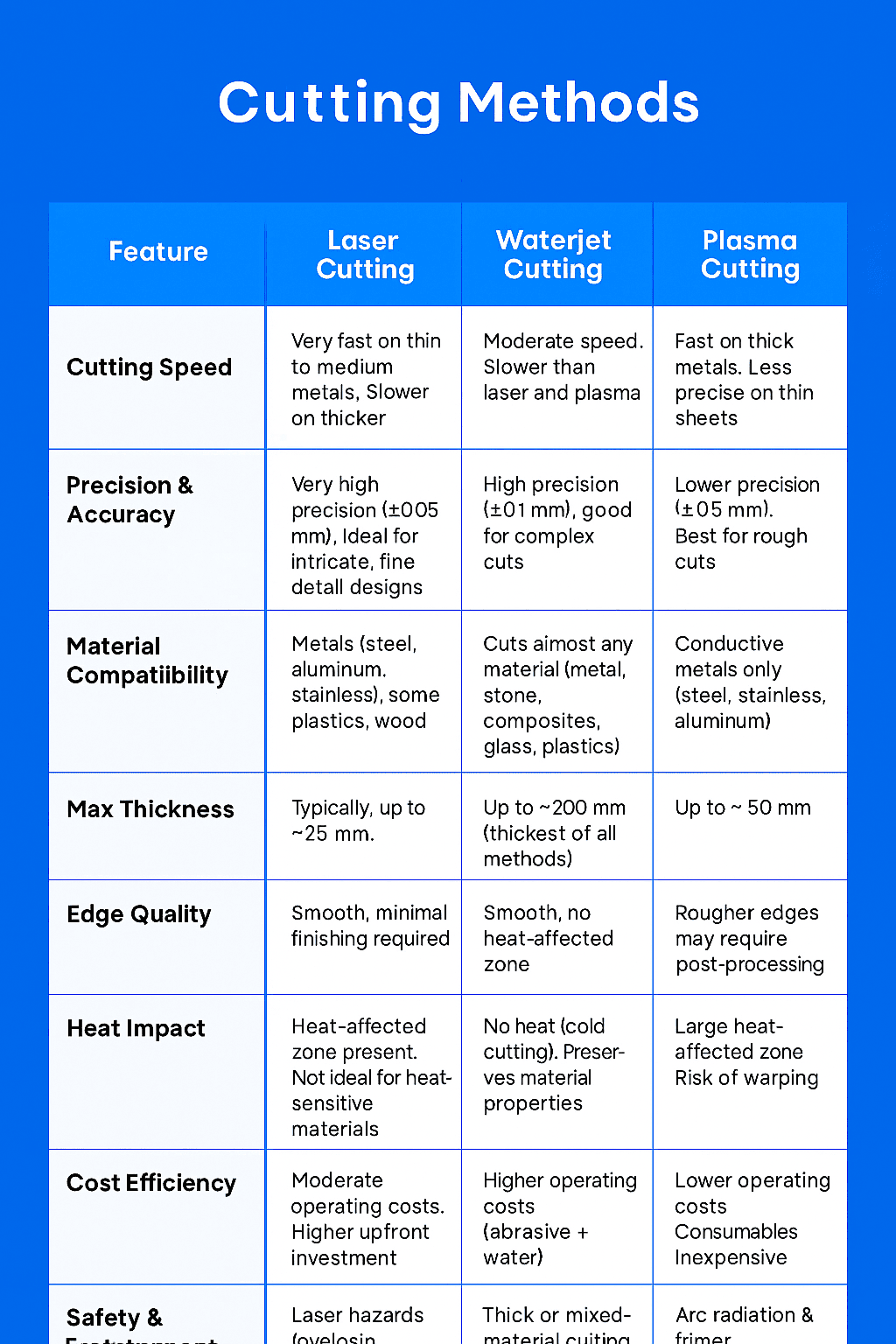
| Cutting Speed | Very fast on thin to medium metals. Slower on thicker materials. | Moderate speed. Slower than laser and plasma. | Fast on thick metals. Less precise on thin sheets. |
| Precision & Accuracy | Very high precision (±0.005 mm). Ideal for intricate, fine detail designs. | High precision (±0.1 mm); good for complex cuts. | Lower precision (±0.5 mm). Best for rough cuts. |
| Material Compatibility | Metals (steel, aluminum, stainless), some plastics, wood. | Cuts almost any material (metal, stone, composites, glass, plastics). | Conductive metals only (steel, stainless, aluminum). |
| Max Thickness | Typically up to ~25 mm. | Up to ~300 mm (thickest of all methods). | Typically up to ~50 mm. |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, minimal finishing required. | Smooth, no heat-affected zone. | Rougher edges may require post-processing. |
| Heat Impact | Heat-affected zone present. Not ideal for heat-sensitive materials. | No heat (cold cutting). Preserves material properties. | Large heat-affected zone. Risk of warping. |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate operating costs. Higher upfront investment. | Higher operating costs (abrasive + water). | Lower operating costs. Consumables inexpensive. |
| Best Applications | Precision parts, thin metals, and intricate designs. | Thick or mixed-material cutting, aerospace, glass, stone. | Structural steel, construction, heavy fabrication. |
| Safety & Environment | Laser hazards (eye/skin protection), fumes require extraction. | High water/abrasive waste. Higher environmental impact if not managed. | Arc radiation & fumes. Requires strong ventilation. |
Pros & Cons of Each Cutting Method
Laser Cutting:
Pros:
- Works on variety of materials, such as metals, plastics, wood, glass, and even some composites.
- Offers very high precision, up to ±0.1 mm, making it excellent for fine and complex shapes.
- Being a non-contact process, there’s little to no contamination of the material from tools or coolants.
Cons:
- The upfront cost of laser cutting machines is quite high, which may not be practical for smaller workshops.
- While it performs really well on thin sheets, it struggles a bit with very thick materials.
- Energy consumption can be higher compared to traditional cutting methods, which may add to operational costs
Waterjet Cutting:
Pros:
- Can cut almost any material like metals, stone, ceramics, composites, plastics, glass, and more.
- It’s a cold cutting process, so the material properties aren’t affected by heat.
- Doesn’t produce harmful fumes, which makes it safer for operators and a bit more eco-friendly.
Cons:
- Cutting speeds are slower compared to laser and plasma.
- The cost of handling high-pressure pumps, abrasives, and maintenance can be quite high.
- Though the waste is non-toxic, disposing of the water-abrasive sludge needs extra effort and equipment.
Plasma Cutting:
Pros:
- Cutting speed is very high, especially since no preheating is required. This means faster turnarounds and better production rates.
- It can cut through rusty, dirty, or even painted metals without needing a clean surface.
- Works well on all conductive metals including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper.
Cons:
- Consumables like electrodes and nozzles wear out quickly, leading to frequent replacements.
- The process generates loud noise, bright sparks, and fumes, so proper protective gear is a must.
- Precision is lower compared to laser, making it less suitable for very detailed or intricate cuts.
Which Cutting Method is Best for Your Project?
- Laser Cutting: Go for laser if accuracy and smooth, clean finishes are your main priority. It’s best suited for thin to medium sheet metals, as well as non-metal materials like plastics or wood. If you’re looking for CNC laser cutting services, this is the method you want.
- Waterjet Cutting: If you’re dealing with very thick materials or ones that can’t handle heat (like stone, glass, or composites), waterjet is the better option. It might be slower, but it leaves a high-quality finish without affecting material properties.
- Plasma Cutting: Pick plasma when precision isn’t the most important thing, but you need speed and cost-effectiveness. As long as your workpiece is conductive metal, plasma will cut through it fast, even if the surface is dirty, painted, or rusty.
Conclusion
Each cutting method has its own unique benefits: laser for precision, waterjet for versatility, and plasma for speed and cost-effectiveness. For projects that demand fine detail, clean finishes, and high accuracy, CNC laser cutting services stand out as the ideal choice.
If you’re based in Pune and searching for laser cutting near me or reliable metal laser cutting services, CNC laser technology offers the perfect balance of quality, efficiency, and consistency for modern manufacturing needs.
Best Laser cutting services by Cyclotron Industries. We offer high precision, fast and accurate laser cutting solutions for any kind of metal applications

Laser cutting services
Laser cutting services in Pune
Fiber laser cutting services in Pune
Metal laser cutting services in Pune
Laser cutting for sheet metal parts
CNC Laser cutting services in Pune