Safety practices in heavy fabrication work
Safety practices in heavy fabrication work
Heavy fabrication is one of the most challenging and high-risk areas in manufacturing. It involves working with thick steel plates, massive structures, and extremely heavy components, all moved by cranes, hoists, and specialized machinery.
Processes such as welding, cutting, bending, rolling, and machining are carried out daily, and each poses its own set of hazards.
- In such an environment, even a small mistake can lead to serious injuries, equipment damage, or costly project delays. That is why safety in heavy fabrication is not just about following rules; it is about building a strong safety culture
- In this blog, we explore the essential safety practices in heavy fabrication, including understanding risks and using protective equipment, safe handling, machine safety, workplace organization, and training.

Best fabrication services by Cyclotron Industries. We offer high precision, fast and accurate fabrication solutions for any kind of metal applications
Understanding Safety Risks in Heavy Fabrication
Before any work begins, it is essential to understand the unique risks involved in heavy fabrication. Here are some of the common risks involved in heavy fabrication:
1. Heavy material handling:
One of the most significant risks is handling heavy materials. Thick plates, beams, and fabricated assemblies are difficult to move, and improper lifting or poor planning can result in serious injuries or material damage.
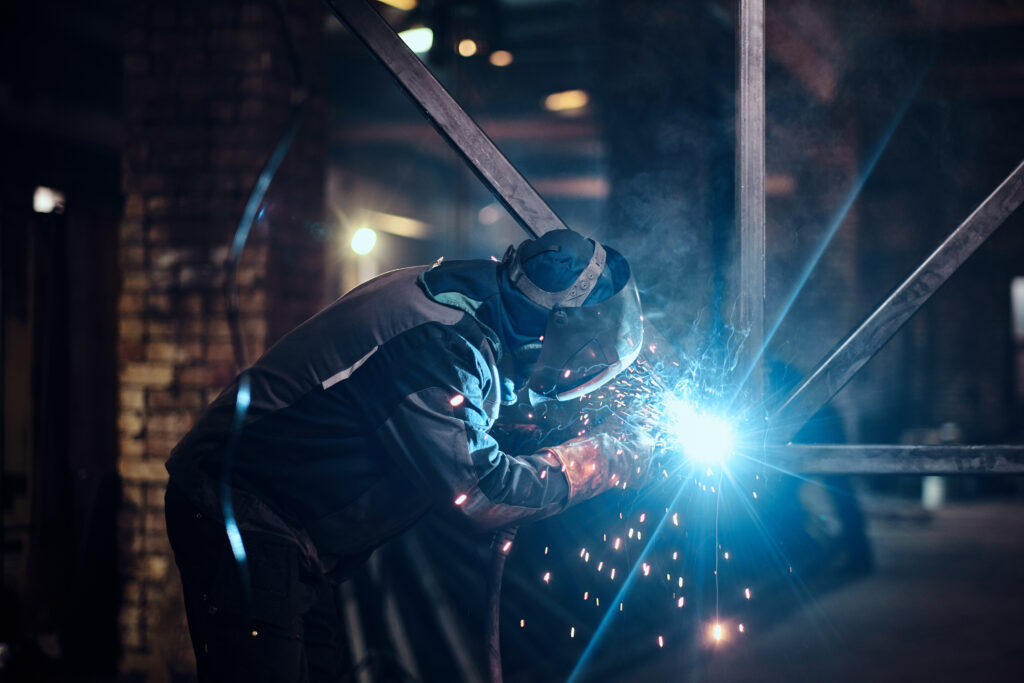
2. Welding and cutting risks:
Welding and cutting operations introduce additional hazards, including intense heat, sparks, fumes, and bright arcs, which can harm workers if proper precautions are not taken.
3. Moving machinery and cranes:
The cranes, forklifts, and rolling machines are essential to fabrication work, but careless operation or poor communication can lead to severe accidents.
There are also fire risks from hot work and flying sparks, as well as structural instability, where large assemblies may collapse if not adequately supported.
Recognizing these risks is the first step toward preventing accidents. When workers understand the risks and respect the power of heavy equipment, they are more likely to follow safe procedures and stay alert on the shop floor.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) in Heavy Fabrication
- Welding helmets, face shields Welding helmets and face shields protect the workers from sparks, molten metal, and harmful UV radiation.
- Safety gloves and shoes Safety gloves and steel-toed shoes help to prevent burns, cuts, and crushing injuries while handling heavy components.
- Flame-resistant clothing Flame-resistant clothing significantly reduces the risk of fire-related accidents, especially during welding and cutting operations.
- Eye and hearing protection Eye and hearing protection safeguard the workers from bright arcs, flying debris, and the constant noise of heavy machinery. When PPE is used correctly and consistently, it allows the workers to focus on their tasks with confidence. Employers must strictly enforce PPE usage, and workers should treat it as a non-negotiable part of their daily routine.
Best fabrication services by Cyclotron Industries. We offer high precision, fast and accurate fabrication solutions for any kind of metal applications
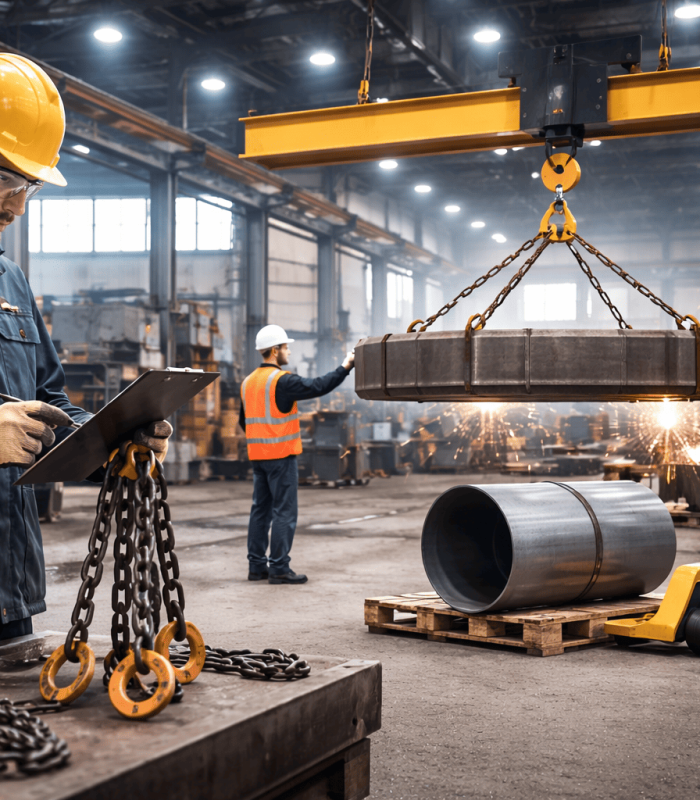
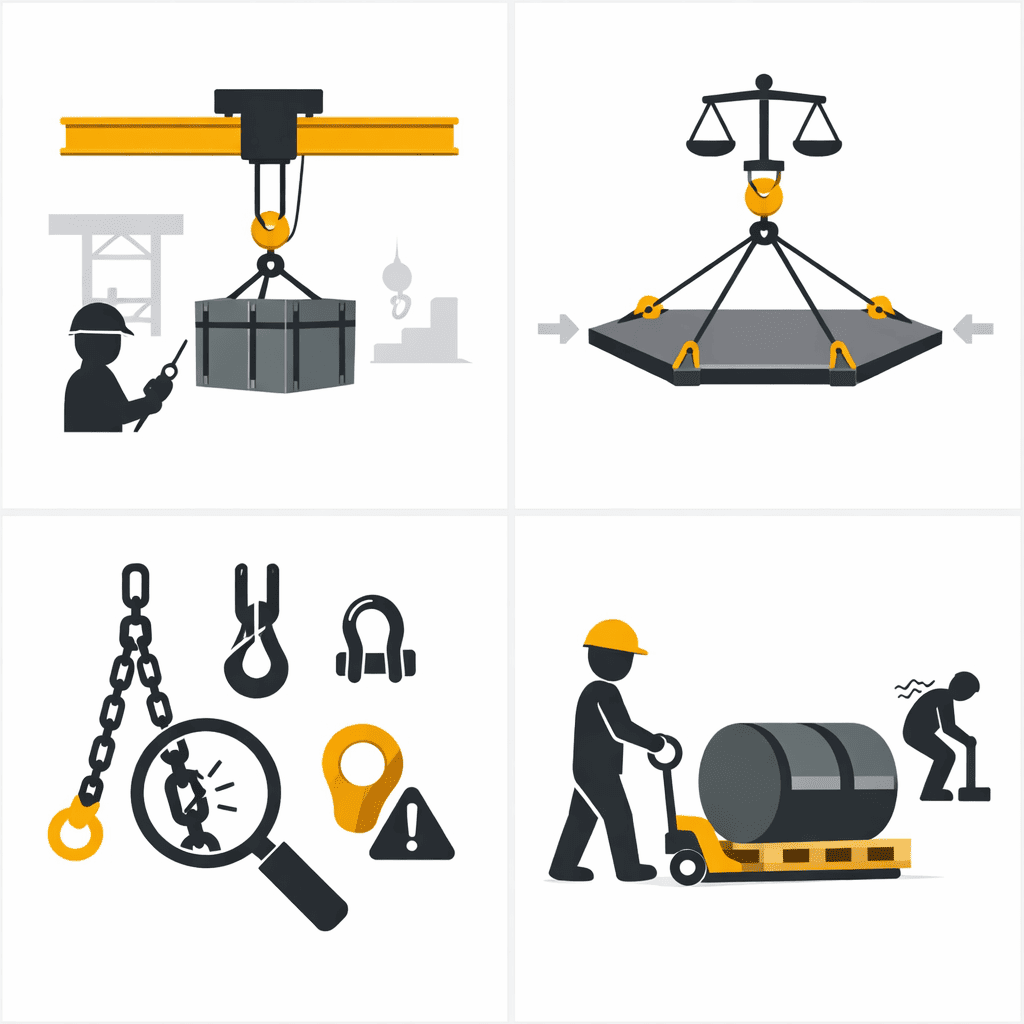
Safe Material Handling and Lifting Practices
Material handling is essential for safety in heavy fabrication work areas.
1.Crane and Hoist Safety
Cranes and hoists are operated by trained and certified personnel. Operators must understand load charts, lifting limits, and safe operating procedures. Overloading cranes or using improper lifting equipment can result in catastrophic failures.
2.Load Planning and Balance
Each lift must be carefully planned to provide proper balance and control, preventing swinging or tipping during movement.
3.Rigging and Sling Inspection
The chains, hooks, slings, and shackles must be inspected regularly for wear, damage, or defects before use.
4.Avoiding Manual Lifting of Heavy Components
The Oversized plates and heavy assemblies should not be lifted manually. Mechanical handling equipment must always be used to reduce the injury risk.
Best fabrication services by Cyclotron Industries. We offer high precision, fast and accurate fabrication solutions for any kind of metal applications
Welding and Cutting Safety Measures
Welding and cutting are at the heart of safety in heavy fabrication, but they also pose some of the highest risks.
Arc welding and gas cutting best practices
Arc welding produces the intense heat, bright light, and harmful fumes, requiring strict safety protocols. Workers must maintain proper electrode angles and travel speeds to prevent excessive spatter and reduce fire risks. Keep welding cables in good condition and inspect them regularly for damage that could pose an electrical hazard.
Gas-cutting operations require careful attention to torch settings and cutting speeds to control the heat-affected zone and minimize dangerous sparks.
Laser and plasma cutting safety protocols
Laser cutting systems generate invisible infrared radiation that can cause severe eye damage even from reflected beams. Install proper enclosures and safety interlocks to prevent accidental exposure.
Plasma cutting produces extremely high temperatures and requires specific safety in heavy engineering work, including proper nozzle selection and proper management of cutting gas.
Both processes create metal fumes and particulates that need immediate extraction.
Fire prevention and spark control systems
Hot work in heavy fabrication generates sparks that can travel up to 35 feet from the cutting point. Install spark screens and fire blankets around work areas, especially when working near combustible materials. Designate fire watchers for high-risk operations and equip them with appropriate extinguishers: Class D for metal fires and Class C for electrical equipment.
Implement hot-work permit systems that require area inspections before and after cutting or welding. Remove flammable materials from the work zone and wet down surrounding areas when necessary.
Trained operator certification requirements
Welding and cutting equipment requires certified operators who understand both the technical and safety aspects of their work. Verify that welders hold current certifications for the specific processes and materials they work with. Gas cutting operators need training in proper torch handling, gas pressures, and emergency shutdown procedures.
Machine and Equipment Safety in Heavy Fabrication
Safety in heavy fabrication work relies on powerful machines that require careful operation and maintenance.
1. CNC Machine Safety
CNC machines should be programmed and verified carefully before operation. Safety interlocks and guards should never be bypassed, even to save time.
2. Plate Bending and Rolling Machine Safety:
Plate-bending and rolling machines create strong pinch points. Guards, emergency stop buttons, and warning systems must be functional and easily accessible.
3. Drilling and Machining Safety:
Loose clothing, gloves, or jewelry can get caught in rotating tools, leading to severe injuries. Operators must follow safe work practices and remain focused during machining operations.
4. Lockout–Tagout and Maintenance Procedures:
Before any maintenance or repair work, machines can be shut down, isolated, locked, and tagged. Lockout tagout procedures prevent accidental start-up and protect maintenance personnel.
Routine inspections and preventive maintenance reduce the breakdowns and improve overall shop safety.
Safety training, supervision and compliance
- Regular Safety Training Programs: The continuous training ensures workers stay up to date on safety procedures, new equipment, and evolving risks. New employees receive a thorough safety induction before starting work
- Toolbox Talks and Daily Briefings: The short, regular toolbox talks help reinforce awareness of task-specific hazards and daily safety priorities.
- Supervision, Audits, and Compliance: Strong supervision ensures safety rules are consistently followed, and regular audits help identify gaps and areas for improvement. Compliance with industry safety standards protects workers and improves the company’s reputation.

Conclusion
Safety in heavy fabrication isn’t just a checklist; it’s a culture that protects lives, equipment, and timelines.
By prioritizing proper handling, PPE, and compliance, fabrication shops can deliver the projects with confidence and reliability.
At Cyclotron, we believe that strong safety practices are the foundation of long-term client trust and industrial excellence.
Explore how Cyclotron integrates safety and innovation into every project: Visit Cyclotron.
Cyclotron group clients



Best fabrication services by Cyclotron Industries. We offer high precision, fast and accurate fabrication solutions for any kind of metal applications

